- Published on
Effectively Using OpenAI's Reasoning Model
- Authors

- Name
- caphe.dev
- @caphe_dev
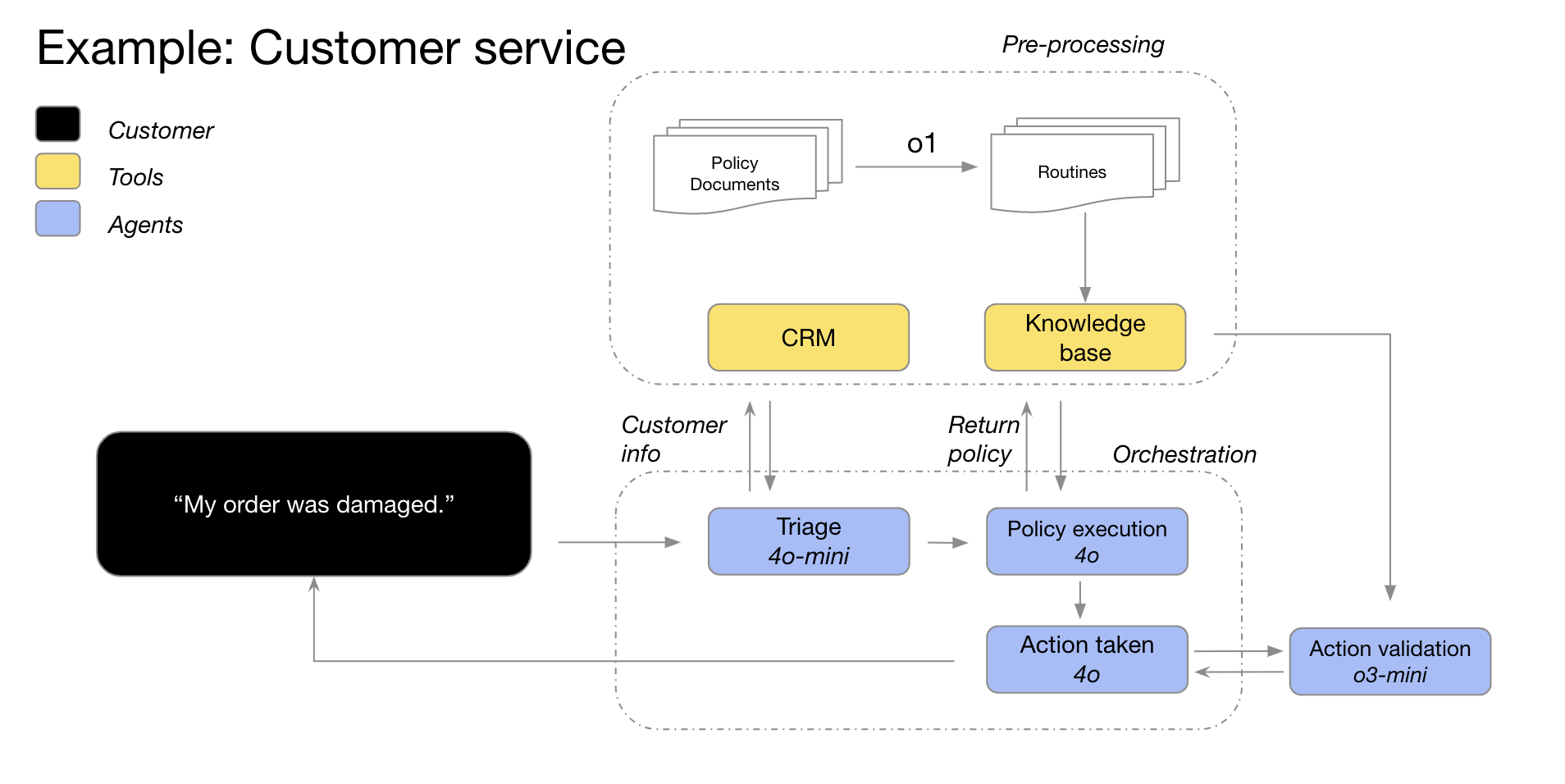
What is a reasoning model?
OpenAI currently has two main types of models:
- Reasoning models: such as o1 and o3-mini
- GPT models: like GPT-4o
Reasoning models are likened to "planners," capable of thinking deeply and long-term about complex issues. They excel at strategizing, planning problem-solving, and making decisions based on large amounts of ambiguous information[1].
Meanwhile, GPT models are likened to "workers," focusing on executing simple tasks quickly and cost-effectively[1].
Examples of the differences between the two types of models:
| Requirement | Reasoning Model (o1) | Standard GPT Model |
|---|---|---|
| "Analyze this financial report and identify potential risks" | In-depth analysis, examining relationships between indicators, providing well-founded warnings | Listing basic indicators, simple analysis |
| "Optimize this code" | Analyzing structure, identifying potential issues, proposing comprehensive solutions | Fixing syntax errors, simple optimization |
| "Plan marketing" | Developing long-term strategies, predicting challenges, proposing solutions | Providing a list of basic marketing activities |
Thus, reasoning models typically provide deeper and more comprehensive analyses, while standard GPT models focus on executing simple tasks quickly[1].
When should you use a reasoning model?
Reasoning models perform well in the following situations:
- Handling ambiguous tasks: They can understand user intent and intelligently fill in gaps in instructions[1].
- Finding a "needle in a haystack": When you need to find important information in a large amount of unstructured data[1].
- Finding relationships in large data: They excel at analyzing complex documents such as legal contracts and financial reports[1].
- Multi-step planning: Reasoning models can act as "planners" in complex AI systems[1].
- Reasoning about images: The o1 model has the ability to understand complex images such as charts and tables[1].
- Evaluating and improving code quality: They are effective in reviewing and improving large amounts of source code[1].
- Evaluating the results of other models: Reasoning models can be used to assess the output quality of other AI models[1].
How to use effectively?
To maximize the power of reasoning models, you should:
- Keep requests simple and direct
- Avoid asking the model to "think step by step"
- Use delimiters to clarify different parts of the input
- Try using the model without prior examples
- Provide specific guidance on the desired outcome - 1. Source